
Private IP addresses, also known as Request for Comment 1918 addresses, are used by most networks today.Again, the device knows what is and what is not on the local LAN by using its assigned subnet mask to compare its local IP address and subnet with the destination's IP address and subnet. A default gateway is a device, typically a router, where hosts send packets that are destined for a device not on the local LAN.A Class D network is used for multicast, and there is an experimental allocation known as Class E. Today, classless IP addresses with variable-length subnet masks are used almost exclusively, and classful IP addresses - known as either Class A network, Class B network or Class C network - are used only for certification testing or older routing protocols.Determining the tradeoff between the number and size of subnets is explained below. An office LAN or data center LAN, however, would use a shorter subnet mask that allows more hosts. For example, a point-to-point link with only two devices would use a 31-bit mask. Organizations will typically use several different subnet masks for different sizes of networks. This increases the number of subnetworks, while reducing the number of hosts per subnet. Subnetting breaks a large network into smaller networks by extending the length of the subnet mask.A longer subnet mask - meaning more 1 bits in the mask - creates more IP subnets that have a smaller host address block size. A subnet mask tells the computer what part of the IP address is the network portion of the address and what part identifies the host address range, which are addresses that are assigned to host computers on that network.The same subnetting procedure works for IPv6 addresses. To calculate the subnet mask, convert an IP address to binary, perform the calculation and then convert back to the IPv4 decimal number representation known as a dotted quad. IPv4 addresses are 32 bits made up of four octets of 8 bits each.
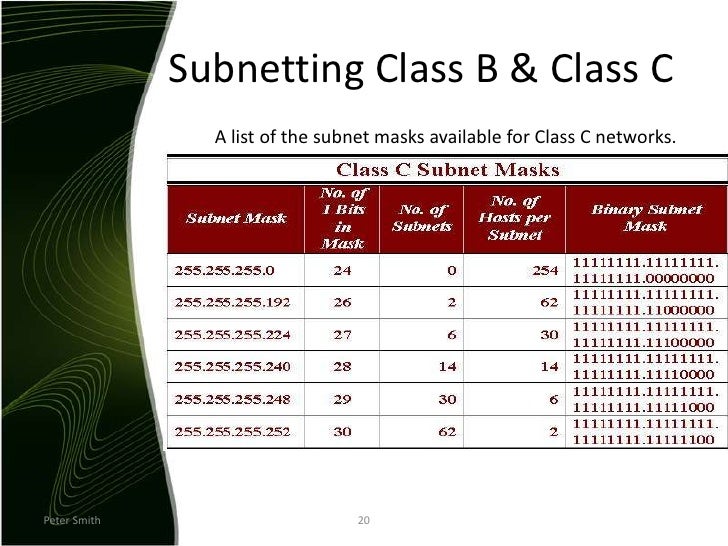

Today, the allocations follow the Classless Inter-Domain Routing ( CIDR) assignment method. ISPs allocate IP address ranges to organizations based on the potential number of networks and hosts, or endpoints, that organizations require.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
